An Airborne Contagious Killer Of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Tuesday, December 8, 2015
Add Comment
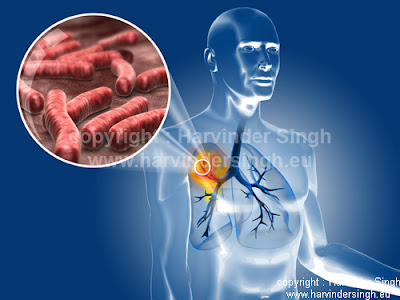
Tubercolosis (also commonly known as TB), is an airborne contagious disease which usually affects the lungs. The symptoms of the TB disease infecting the lungs include coughing with sputum tinged blood, chest pains on exertion, fever, fatigue, weight loss, weakness, aches and chills. The treatment for uncomplicated cases of tuberculosis is the anti-tuberculosis medication taken for the duration of six months. TB is caused by the bacteria known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
TB is passed from person to person via tiny droplets of mucus or saliva containing the bacteria. If someone with a weakened immune system inhales the tiny infected airborne droplets, the bacteria goes straight into the lungs and may cause serious illness that can lead to death.
TB is passed from person to person via tiny droplets of mucus or saliva containing the bacteria. If someone with a weakened immune system inhales the tiny infected airborne droplets, the bacteria goes straight into the lungs and may cause serious illness that can lead to death.
TB is a real killer among people who have weakened immune systems, especially patients who have chronic lung disease or people who are HIV positive. It is a contagious disease that spreads through the air and was declared a worldwide pandemic stage in 2007 with new cases diagnosed of over 9 million people!
In efforts to eradicate this global deadly disease, the World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of proper health care systems and the need for effective primary heath care to address the TB epidemic. It includes integrated health care systems involving the community such as the DOTs (Directly Observe Treatment short course) strategy.
In efforts to eradicate this global deadly disease, the World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of proper health care systems and the need for effective primary heath care to address the TB epidemic. It includes integrated health care systems involving the community such as the DOTs (Directly Observe Treatment short course) strategy.
This involves the caretakers or family members staying with the patient watching the patient taking the medication on time and actually swallowing it. If the medication is not taken on time, or the patient avoids the medication, this may cause the bacteria to become drug resistant and form a new strain. This strategy is found to be a very effective step to ensure the compliance for the cure and eradication of the TB disease. An indoor air purifier can be installed in the home to minimize the number of airborne TB bacteria in the air when the patient coughs, sneezes, talks or even breaths heavily.












0 Response to "An Airborne Contagious Killer Of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis"
Post a Comment